How Does a Section 1042 Election Work?
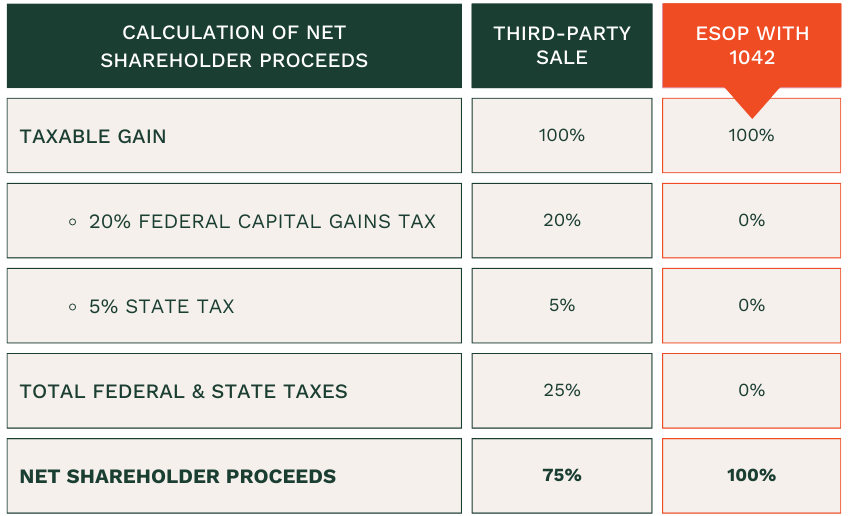
A Section 1042 election allows the selling shareholder to defer capital gains tax by “rolling over” the proceeds from the sale of stock into Qualified Replacement Property (QRP). This rollover must take place either 3 months before the ESOP transaction or within 12 months after the sale.
Think of the 1042 election as similar to a 1031 exchange in real estate, where the seller can defer taxes by reinvesting in a like-kind property. For 1042, the shareholder sells their stock in the company to an ESOP and reinvests the proceeds into QRP.
For more detail on QRP and how tax deferral works in an ESOP transaction, click here.
Key Requirements for a Section 1042 Election
To qualify for a Section 1042 election, certain criteria must be met. However, most are commonly achieved during the ESOP transaction.
- 30% Ownership: The ESOP must own at least 30% of the company after the transaction.
- Stock Origin: The selling shareholder cannot have received stock to be sold to the ESOP from:
- a retirement plan
- pursuant to a stock option
- as restricted stock
- as a form of compensation
- Holding Period: Minimum 3-year ownership period for stock sold to the ESOP
- Corporate Structure: The company must be a non-publicly traded C corporation at the time of the sale.
- Reporting Type: Must be a non-publicly traded C corporation at the time of the ESOP sale transaction
- Stock Type: Common stock having the highest voting and dividend rights, or preferred stock convertible into such common stock
- Tax Filings: Statements of Election, Consent and Purchase must be filed with the shareholder’s tax return for the year in which the sale occurred
For business owners considering an ESOP, understanding the potential tax savings from a Section 1042 election is a critical step in planning for a successful transition.
Learn why Section 1042 was created to support both economic impact and retirement security, and how business owners can defer capital gains taxes by reinvesting sale proceeds into Qualified Replacement Property (QRP).
Explore Lazear’s proprietary 1042 tax solution by clicking here.